
|
Type B: Ripped or corrugated wall construction: A pipe or a fitting with plain internal surface and a solid or hollow spiral or annular profiled external surface shall be designated Type B: (Image: View of an extruded solid wall pipe with ribbed outer surface) (Image: View of an extruded solid wall pipe with ribbed outer surface) |

|
Scope of application Pipes that are composed of an extruded solid wall system with ripped or corrugated outer surface are joined by means of sockets. Their manufactured lengths are 2,000, 3,000 and 5,000 mm. The pipes have a plain inner surface and a concentrically ribbed outer surface. (Image: View of an extruded solid wall pipe with ribbed outer surface) (Image: Elevation and section of an Ultra-Rib sewage pipe with pipe joint [FI-Upono]) |

|
Spiral-wound pipes are made of PVC-U, PE or PP by means of a winding process and are provided with a screw-shaped circumferential profile reinforcement or as a double-wall profile; whereby the inner surfaces of the pipes are always smooth. Spiral-wound pipes of PE are defined and described in DIN 16961 and also in PAS 1065. [DIN16961-1:2011] [PAS1065] (Image: Longitudinal section through spiral pipes (Bauku GmbH) [FI-Bauku]) |

|
Glass fibre reinforced plastics (GRP) are among the thermosetting plastics, which are no longer fusible by temperature influence. Basic raw materials for GRP are thermosetting resins (epoxy, vinyl ester or unsaturated polyester resin) which are used as binders and, glass and quartz sand and calcium carbonate powders which are used as aggregates The latter two components are referred to as fillers, additives for increasing the volume of the mixture … |

|
Glass fibre reinforced plastics usually consist of two components, resin and glass fibres. The addition of fillers is possible. The resin used is primarily polyester resin and epoxy resin is also used in small quantities. In the given case of application, the glass fibre reinforcing is primarily used in the form of -
Mats (unwoven mats of cut or uncut glass fibres which are glued or mechanically bound on a carrier material),
-
Weaves (manufactured on …
|

|
The following methods are used in the manufacture of pipes and fittings made of GRP [Grüne72] [Himml81]: Hand lamination In this process, used mainly for the production of fittings but also for pipe joints, glass fibre mats or weaves are placed on a mould or the component and the resin is applied and spread by hand. Fibre spray method Simultaneous spraying of resin, glass fibre cut from roving and filler materials onto a mould. The work is carried out … |

|
Two different variations can be distinguished for this method: Option 1: Inserting a glass fibre mat by hand into a wooden cylinder (mould). This is then put into rotation and the resin is then added at the same time by means of a pipe. Option 2: The resin, the cut glass fibre, as well as the filler material are inserted into the rotating mould by means of a special insertion arm. This is done either all together or in the desired sequence, so that … |

|
(Image: Structure of a pipe wall of a GRP pipe cast by the centrifugal spray method (option 2)) |

|
What defines the mechanical properties of GRP pipes? The mechanical properties of GRP pipes are determined by Schlehöfer and Grünwald [Schle73] [Grüne72]: The adhesion between resin and fibres, The type, content and position of glass fibres and The percentage of fillers. (Image: GRP jacking pipe) The pipe stiffness, which is relatively low when resin and fibres are used exclusively, can be adjusted to the respective requirements by integrating layers with … |

|
Pipes made of glass fibre reinforced plastics (GRP) have been produced since the start of the 1960s. Originally, they were used for the discharge of aggressive effluents in industrial undertakings but then became increasingly important in the sewage sector where they are laid today |
|
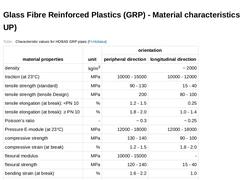
(Table: Characteristic values for HOBAS GRP pipes) |

|
(Image: Cast iron pipe) Cast iron piping has been used for more than 500 years, originally as grey cast iron piping. They were primarily used for the conveyance of drinking and process water [Biere85]. With the start of gas supplies more than 100 years ago, cast iron piping was used for this purpose as well. Because of their excellent sound absorption characteristics, grey cast iron pipes without sleeves in the sewage sector are primarily used as drain … |

|
Unprotected and earth-covered piping of ductile cast iron can be damaged by corrosion from the outside as well as the inside when they come into contact with oxygen-enriched, watery media. Hence, such pipes must be provided with an outer and inner corrosion protection when used in the water or sewage sectors. (Image: Hole corrosion - pitting) |

|
(Image: Cast pipe with external corrosion protection in the form of cement mortar coating) Protective internal linings and external coatings are often applied to ductile cast iron pipes to prevent corrosion Coatings of zinc or a zinc-aluminium alloy with a top coat of epoxy resin are standard for the outside corrosion protection of the pipes [EN545:2011], [EN598:2009]. The following coatings are offered for ductile cast iron pipes that are laid into … |

|
(Image: Cast pipe with internal corrosion protection in the form of cement mortar lining) The internal corrosion protection must be in the form of a cement mortar coating [DIN2880:1999], [EN545:2011]. According to DIN 2880 and DIN EN 598, aluminate cement is specified as standard in the field of sewerage in order to provide a greater resistance to sulphates. Usually, the layers are 4 mm thick for DN 80 to DN 300, 5 mm for DN 350 to DN 600, 6 mm for … |

|
The field of application for ductile cast iron pipes is specified in DIN EN 598, which is the decisive standard for sewers. According to that standard they are not only permitted for gravity piping covered with earth but also for pressure pipes in the range DN 80 to DN 2000. [EN598:2009] According to DIN EN 598, sewage pipes made of ductile cast iron are produced in the nominal sizes DN 80 to 2000 with lengths of 6,000 mm (for DN ≥ 700 also 7,000 … |

|
|

|
Pipe joints must be leak tight against internal and external water pressure. Movable (flexible) pipe joints (must also be leak tight at the maximum permissible deflection. All parts of the pipeline including the pipe joints and sealings must be designed, produced and examined according to the objective to guarantee the tightness during the construction works (construction state) and the whole planned service life (operation state) … |

|
Demands on the pipe joints of jacking pipes (Image: Icon: Watertightness) Tightness against internal and external pressure (Image: Transfer of the longitudinal force) Transfer of the longitudinal force by securing the lateral stability (Image: Corrosion protection end faces of the pipe) Corrosion protection of the end faces of the pipe |

|
In the following, both historical and current pipe joints in sewage systems are presented. In general these pipe joints were divided into the following |

|
Plug joint A plug joint (in practice also called a socket-and-spigot -joint) is a flexible pipe joint. Spigot and sockets involve a normal pipe end, the spigot, being inserted into the socket or bell of another pipe or fitting with a seal being made between the two within the socket. Clamp joint A clamp joint is a flexible pipe joint whose sealing effect is achieved by clamping a sleeve over the pipe ends to be … |

|
(Image: Stuffing box joint) Stuffing box joint A stuffing box joint is a flexible pipe joint whose sealing effect is achieved by plugging together the spigot end and the socket and then pressing in an elastic sealing medium by means of a follower nut. Adhesive joint An adhesive joint is a pipe joint whose sealing effect is achieved by gluing together the pipe ends that are to be connected. Depending on the type of the applied adhesive … |

|
Welded joint A welded joint is a rigid pipe joint whose sealing effect is achieved by welding the pipe ends together. Flanged joint A flanged joint is a rigid pipe joint whose sealing effect is achieved by placing a sealing medium between the flanges. (Image: Pipe joint with elastic sealing medium) Elastic sealers Elastic sealers are sealers composed of elastomers (see DIN 7724 [ [DIN7724:1993]]), that are inserted … |
|
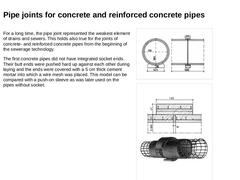
For a long time, the pipe joint represented the weakest element of drains and sewers. This holds also true for the joints of concrete- and reinforced concrete pipes from the beginning of the sewerage technology. The first concrete pipes did not have integrated socket ends. Their butt ends were pushed hard up against each other during laying and the ends were covered with a 5 cm thick cement mortar into which a wire mesh was placed. This model can … |

|
The tongue and groove joint consists of a tongue and groove fabricated on matching pipe ends to provide some indexing when the two pipe ends were assembled. This joint was the most common in use for concrete pipes. DIN 1201 supplementary sheet, February 1923 “Sewerage pipes of concrete” specifies that “a better joint has not been found to this day”. The approach to standardise this joint seemed unacceptable in the past. It was only demanded that … |