|

|
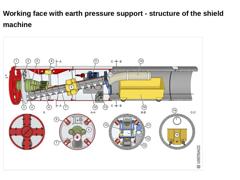
(Image: Earth pressure balance shield of type EPB 1500 (external diameter 1830 mm) with transport cart with reference to [FI-Herreb] [Image: S&P GmbH] - Longitudinal and cross sections) |
|

|

|
(Image: Attention!)
The support pressure is indirectly monitored by the speed of rotation of the spiral and the variably adjustable opening cross-section of the discharge slide gate between the auger and the discharge pipe (A cladding tube at the end of the spiral conveyor with an opening for the discharge of the conveying medium [Herre01]) and thus the conveying quantity of the spiral conveyor as well as the jacking speed, is regulated with the … |
|

|

|
(Table: Demands on the subsoil and mud for the use of earth pressure balance shields ) |
|

|

(Image: Possibilities of foam conditioning - Sketch of principle - Test run of a shield machine DN/ID 1500 in the works [FI-Herreb]) If the consistency of the excavated soil is insufficient, or if the application limits of the shield machines are be extended to non-cohesive and inhomogeneous soils, the preferred area of application of EPB shields, then the soil must be artificially conditioned. Suitable additives for this are: -
Water
-
Suspensions based …
|
|

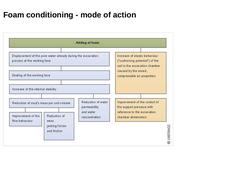
(Image: Mode of action of foam conditioning) |

|

From a process point of view, the limit of application of an EPB shield with foam conditioning is reached when one of the following cases occur: |
|
Application limit of an earth pressure balance shield with foam conditioning - case 1: -
By injecting a highly viscous foam, no sufficient support pressure can be created.
-
Causes: particle distribution is too coarse or compactness of the soil is too low
-
Consequence: foam only escapes through the working …
|
|

|

Critical operating conditions of an EPB shield can occur even through small deviations of balance conditions, with excavation chamber overpressure as well as with under-pressure. What may be the causes of critical operating states? (Image: Question) What may be the consequences of critical operating states? (Image: Question) |

|

Critical operating conditions of an EPB shield can occur even through small deviations of balance conditions, with excavation chamber overpressure as well as with under-pressure. Causes of critical operating states: -
operating errors of the shield machine
-
too late adaption to changing subsoil conditions
Consequences of critical operating conditions: -
crown collapse
-
subsidence
-
break into the open
-
machine downtime
|

|

(Table: Operating conditions of the earth pressure balance shield [FI-Steina]) |
|

|

| (Image: EPB shield with incomplete filling of the working chamber with danger of caving (Condition 2a) with reference to [Wilms95] [Image: S&P GmbH]) Critical operating condition - condition 2a - results from a too high soil removal
- the upper area of the excavation chamber is not filled
- correction via change of the torque of the spiral conveyors
- danger: crown collapse with corresponding subsidence at the ground surface
| (Image: EPB shield with hardened material … |
|

|

Critical operating condition - Condition 3 -
Results directly from condition 2a or also after longer downtimes.
-
The excavation chamber is incomplete and the upper area is filled with water.
-
Danger: water enters the area of the spiral conveyor and causes liquid to muddy consistencies of the mud.
-
Pressure-balancing function of the spiral conveyor cannot be maintained.
-
Increased danger of crown collapse up to breaks into the open.
|
|
|
|
(Image: EPB … |
|

|

Critical operating condition - Condition 4 -
Results from a too low conveying performance of the spiral conveyor.
-
Solidification of the mud in interaction with the agitating of the cutting wheel, especially in and first in the central region, caused by the excessive pressure in the excavation chamber.
-
Consequence: sticking of machine parts up to downtime of the machine (condition 5).
|
|
(Image: EPB shield with compaction of the mud in the excavation … |
|

|

Critical operating condition - Condition 5 -
Resulting from condition 4 if the too low conveyor performance of the spiral conveyor is not immediately corrected.
-
With growing torque and reducing jacking speed the mud warms up increasingly.
-
Warming increasingly affects the solidification and sticking tendency.
-
In an extreme case the solidification reaches the entire excavation chamber starting from the centre of the excavation chamber.
-
Consequence: …
|
|

|

| (Image: Operating condition when encountering an obstacle (Condition 6) with reference to [Maidl97b] [Image: S&P GmbH]) Critical operating condition - Condition 6: Encountering an obstacle - When encountering an obstacle (e.g. a boulder), the contact pressure force must be increased.
- Consequence: control and transfer of the required support pressure from the pressure bulkhead via the mud in the surrounding subsoil is immensely impaired.
| (Image: EPB shield … |
|

|

|

|

(Table: Obstacle removal in pipe jacking with partial excavation [FI-Steina]) |
|

|

(Table: Obstacle removal in pipe jacking with full-face excavation [FI-Steina]) |
|

|

|
(Table: Obstacle removal in pipe jacking (special forms)) |
|

|

|

|

|
(Image: Attention!)
If the method is changed, the principle of supporting the working face during jacking is changed. By doing so the technique-specific limits of application can be shifted and/or extended. |
|
It is distinguished between: -
unscheduled change of method by modification
-
schedules change of method by modification
-
scheduled change of method by conversion.
[Tunnel01] |
|
In all cases, access is necessary for carrying out the required mechanical … |
|
|

Unscheduled changes of the method by means of modification are carried out from the pipe string or from a specially excavated auxiliary shaft. |
|
(Image: Pros and cons) |
Disadvantages of unscheduled changes of the method by modification: -
the modification is labour-intensive and time-consuming (might take weeks)
-
causes high costs due to the delay of the construction project
-
ground stabilisation measures might have to be taken
|
|
|
|
|
(Image: Attention!) |
|
|

| (Image: Attention!) An expected or scheduled change of method technology must be taken into account early on in the planning phase. | | If modification in the shaft is not possible due to topographical or other reasons, then it is carried out in the protection of a specially built station through the pipe string [Tunnel01]. | | (Image: Pros and cons) | Disadvantages of scheduled change of method by modification: - modification is labour-intensive and time-…
|
|
|

|

|
(Image: Attention!)
A scheduled change of method by conversion can only be carried out with shield types that are further developed for this purpose. |
|
(Image: Pros and cons)
Advantages of scheduled change of method by conversion: -
conversion can take place in each spot of the jacking route
-
relatively short conversion times if the subsequent material conveying does not have to be changed
|
(Image: Pros and cons)
Disadvantage of scheduled change of … |
|

|

(Table: Conventional changes of method by conversion in pipe jacking [Tunnel01]) |
|

|

|