
|
(Bild: Muffenprüfgerät in einem nicht begehbaren Querschnitt) (Bild: Luftaustritt aus der Rohrwandung während der Prüfung) Aufgrund des relativ kleinen Prüfraumes wirken sich bereits geringe Umläufigkeiten zwischen Absperrelement und Rohrwandung stark auf das Ergebnis der Einzelmuffenprüfung aus. Da bei den herkömmlichen Prüfgeräten in der Regel nur der Prüfdruck innerhalb des Prüfraumes überwacht wird, kann nicht unterschieden werden, ob tatsächlich … |

|
Um das Problem des Nachweises der ausreichenden Dichtwirkung der Absperrelemente zu lösen, wurden spezielle Prüfgeräte entwickelt, welche an beiden Enden jeweils zwei Absperrelemente (Doppelpacker) aufweisen, zwischen denen in einem „Referenzprüfraum“ vor der eigentlichen Muffenprüfung zunächst die Abdichtwirkung der Absperrelemente überprüft werden kann. Ein Beispiel hierfür zeigen die Bilder: (Bild: Muffenprüfgerät für nicht begehbare Nennweiten … |

|
(Video: Muffenprüfgerät in Anlehnung an den Duo-Mupp von Städtler+Beck) Video: Muffenprüfgerät in Anlehnung an den Duo-Mupp von Städtler+Beck [Bild: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stein & Partner GmbH]. Dieses interaktive Objekt ist ausschließlich in der Online-Version des Moduls sichtbar. |

|
Bei begehbaren Abwasserleitungen und -kanälen erfolgt die Positionierung der Muffenprüfgeräte in der Regel manuell, d.h. Antriebseinheit und Kamerabeobachtung sind nicht erforderlich. Muffenprüfgeräte für begehbare Profile sind für nahezu alle Standard- und Sonderprofile erhältlich. (Bild: Muffenprüfgerät für einen Sonderquerschnitt) (Bild: Muffenprüfgerät für den begehbaren Nennweitenbereich [FI-Städt]: Rinnenquerschnitt mit einseitigem Auftritt) (… |

|
Die Prüfgeräte besitzen einen ringförmigen Prüfraum und bestehen insbesondere bei größeren Nennweiten in der Regel aus mehreren Segmenten, welche nach dem Einbringen über einen Schacht im Kanal montiert werden. Die Abdichtung des Prüfraumes gegen die Rohrwandung erfolgt durch zwei umlaufende Gummidichtungen, welche mit Luft aufgeblasen werden. (Bild: Arbeitsschritte beim Prüfen einer Rohrverbindung mittels eines Muffenprüfgeräts in Anlehnung an [FI-… |

|
Der Arbeitsablauf bei der Durchführung der Dichtheitsprüfung einzelner Rohrverbindungen wird nachfolgend für die in begehbaren Kanälen erläutert. (Bild: Muffenprüfgerät für den begehbaren Nennweitenbereich [FI-Städt]) (Bild: Muffenprüfung im begehbaren Nennweitenbereich) Diese Arbeitsgänge müssen im nicht begehbaren Nennweitenbereich ferngesteuert und unter ständiger Kamerabeobachtung durchgeführt werden. (Bild: Muffenprüfung im nicht begehbaren Nennweitenbereich - … |

|
Vor dem Einsatz von Muffenprüfgeräten im Kanal ist oberirdisch eine „Nullmessung“ in einem mitgeführten, kurzen Rohrabschnitt vorzunehmen, um die Dichtheit des Prüfsystems zu testen [DWAA139:2009]. (Bild: Test des Muffenprüfgerätes (Nullmessung) an einem nicht verbauten Kanalrohr) |

|
Das Prüfgerät wird auf einem Fahrgestell zum Einsatzort gezogen oder geschoben und dort mittig über dem Fugenspalt platziert. Die Abdichtung erfolgt durch zwei Abdichtungsprofile (Gummihohlprofile oder -schläuche), die mit 4 bis 8 bar aufgepumpt und dabei fest gegen die Rohrinnenwände beiderseits der Rohrverbindung gepresst werden. (Bild: Arbeitsschritte beim Prüfen einer Rohrverbindung mittels eines Muffenprüfgeräts in Anlehnung an [FI-KMG] [Bild: … |

|
Für den Einbau des Prüfgerätes muss die Kontaktfläche zwischen Absperrelement und Kanalwandung gereinigt und bei stark porenhaltigen Betonoberflächen vorbehandelt werden. Durch die Möglichkeit der direkten optischen Kontrolle können Umläufigkeiten zwischen dem Prüfgerät und der Rohrwandung erkannt und so Verfälschungen der Prüfergebnisse in der Regel vermieden werden. Zur besseren Erkennbarkeit möglicher Undichtigkeiten bietet sich der Einsatz von … |

|
Umläufigkeiten im Beton können aufgrund einer Porosität im Betongefüge und / oder aufgrund von Bewehrungsschatten entstehen. Bewehrungsschatten können während des Herstellungsprozesses von Betonrohren entstehen, wenn es zu Vibrationen des Bewehrungskorbes während des Herstellungsprozesses kommt. In der Konsequenz führen diese zu Umläufigkeiten entlang des Bewehrungskorbes, mit der Folge von Undichtigkeiten an Stellen geringer Betonüberdeckung oder … |

|
(Bild: Betonrohr mit Keralineauskleidung und Hohlräumen im Verbundbereich) Bei Betonrohren mit einer Auskleidung kann es ebenfalls zu Umläufigkeiten durch Hohlräume im Verbundbereich zwischen Rohrwandung und Auskleidung kommen, die eine Interpretation der Prüfergebnisse erschweren bzw. unmöglich machen. |

|
Die Dichteitsprüfung einzelner Rohrverbindungen mit dem Prüfmedium Wasser wird in der DIN EN 1610 [EN1610:2015] bzw. im DWA-A 139 [DWAA139:2009] für neu verlegte Abwasserleitungen und -kanäle geregelt. Hiernach gelten für die Prüfung einzelner Rohrverbindungen dieselben Prüfkriterien, d.h. die gleichen Wasserzugabewerte und Prüfzeiten, wie bei der haltungs- bzw. abschnittsweisen Dichtheitsprüfung: -
Prüfzeit: 30 min
-
zulässige Veränderung des Wasservolumens: …
|

|
Die Prüfzeit von 30 min pro Rohrverbindung ist zu beachten. So ergibt sich beispielsweise für die Prüfung aller Rohrverbindungen eines 27,5 m langen Prüfabschnittes bei einer Rohrlänge von 2,5 m (12 Rohrverbindungen) eine reine Prüfzeit von 6 Stunden. (Bild: Beispiel für die Summierung der Prüfzeiten bei der Prüfung einzelner Rohrverbindungen einer ganzen Haltung) |

|
Eine Reduzierung der Prüfzeiten von 30 auf 10 min erlaubt das DWA-A 139 [DWAA139:2009] für Querschnitte > DN 1000 (vgl. Tabelle). In diesem Fall ergibt sich die Notwendigkeit, extrem geringe Volumenströme messen zu müssen. Bei Rohren ≤ DN 1000 würde eine Verkürzung der Prüfzeiten wegen der sich daraus ergebenden sehr geringen Wasserzugabemengen zu keinem praxisnahen Prüfergebnis führen [DWAA139:2009]. (Tabelle: Prüfungsanforderung für die Dichtheitsprüfung … |
|
Warum gibt es kein allgemeingültiges Dichtheitskriterium für die Prüfung einzelner Rohrverbindungen mit Luft? Da die Abmessungen der Muffenprüfgeräte und damit das Prüfraumvolumen je nach Hersteller variieren, ist es nicht möglich, ein allgemeingültiges Dichtheitskriterium zu entwickeln. In diesem Zusammenhang ist es daher unabdingbar, für jedes Muffenprüfgerät im Vorfeld der Prüfungen das Prüfraumvolumen zu ermitteln und über dieses mit Hilfe … |

|
Zur Ermittlung der erforderlichen Prüfzeiten muss das Prüfraumvolumen des eingesetzten Muffenprüfgerätes einschließlich des Volumens der zuführenden Schläuche (falls diese während der Prüfung eine Verbindung zum Prüfraum aufweisen) sowie das Volumen der Rohrverbindung ermittelt werden. Bei nicht begehbaren Abwasserleitungen und -kanälen kann im Allgemeinen auf die Ermittlung des Volumens der Rohrverbindung verzichtet werden. |
|
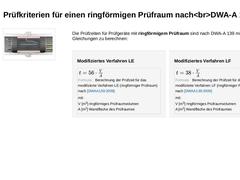
(Bild: Schematische Darstellung eines Muffenprüfgerätes mit ringförmigen Prüfraum in Anlehnung an DWA-A 139) Die Prüfzeiten für Prüfgeräte mit ringförmigem Prüfraum sind nach DWA-A 139 mit folgenden Gleichungen zu berechnen: Modifiziertes Verfahren LE (Formel: Berechnung der Prüfzeit für das modifizierte Verfahren LE (ringförmiger Prüfraum) nach DWA-A 139 (2009)) Modifiziertes Verfahren LF (Formel: Berechnung der Prüfzeit für das modifizierte Verfahren … |

|
Erfolgt die Prüfung im Grundwasser, d.h. der Grundwasserspiegel liegt oberhalb des Rohrscheitels, so ist dessen Einfluss bei der Prüfung zu berücksichtigen. DIN EN 1610 [EN1610:2015] schreibt in dem Fall entweder eine Infiltrationsprüfung oder eine Prüfung mit höherem Druck vor. Bei einer Prüfung mit höherem Druck ist der Prüfdruck pro 10 cm Grundwasser über der Rohrsohle um 1 kPa zu erhöhen [DWAA139:2009]. Nach DWA-A 139 wird der Prüfdruck aus sicherheitstechnischen … |

|
Nach Ablauf der Prüfzeit, d.h. am Ende der Prüfung erfolgt die Feststellung tatsächlichen Druckdifferenz. Die Prüfung gilt als bestanden, wenn -
die Veränderung des Wasservolumens einen festgelegten Grenzwert nicht überschreitet (Wasserdruckprüfung)
-
bzw. die vorhandene Druckdifferenz Δp ≤ zulässige Druckdifferenz aus DIN EN 1610 oder DWA-A 139 erfüllt.
(Bild: Prüfprotokoll einer bestandenen Muffenprüfung mit Luft) Nach erfolgter Prüfung wird der Druck … |
|
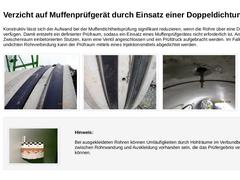
Konstruktiv lässt sich der Aufwand bei der Muffendichtheitsprüfung signifikant reduzieren, wenn die Rohre über eine Doppeldichtung verfügen. Damit entsteht ein definierter Prüfraum, sodass ein Einsatz eines Muffenprüfgerätes nicht erforderlich ist. An einen im Zwischenraum einbetonierten Stutzen, kann eine Ventil angeschlossen und ein Prüfdruck aufgebracht werden. Im Falle einer undichten Rohrverbindung kann der Prüfraum mittels eines Injektionsmittels … |

|
|

|
Gibt es generelle Anforderungen bezüglich der Qualifikation des mit der Prüfung betrauten Personals? In Anbetracht der Bedeutung der Dichtheitsprüfung generell und der mit der Prüfung verbundenen Gefahren werden besondere Anforderungen an die Qualifikation des mit dieser Aufgabe betrauten Personals gestellt. So sind nach DIN EN 1610 [EN1610:2015] bei der Verlegung und Prüfung von Abwasserleitungen und -kanälen nachfolgende generelle Anforderungen … |

|
(Bild: Gütesicherung Kanalbau mit Güte- und Prüfbestimmungen (2016)) Das DWA-A 139 Abschnitt 13.1 „Verfahren und Anforderungen für die Dichtheitsprüfung von Freileitungen“ konkretisiert diese Forderungen wie folgt [DWAA139:2009]: Die durchführenden Unternehmen müssen ihre Eignung nach RAL-GZ 961, Gruppe D „Güteschutz Kanalbau“ [RALGZ961] oder nach DWA-M 190 [DWAM190 (2014)] nachweisen. Die Prüfung muss von einem Aufsichtführenden geleitet werden, dessen … |

|
|

|
Herzlichen Glückwunsch! Hiermit haben Sie die vorliegende Lektion erfolgreich beendet. Im Anschluss haben Sie nun die Möglichkeit, das neu erlangte Wissen mithilfe eines interaktiven Fragebogens selbstverantwortlich zu überprüfen. Natürlich können Sie außerdem nach wie vor zu einem beliebigen Punkt in den vergangenen Lektionen zurücknavigieren, um das eine oder andere Thema oder Detail erneut anzuschauen. Bleiben Sie neugierig! |