
|
(Image: Design of a heated tool or butt fusion welded joint (vertical down weld) [349])Due to the high economic efficiency and the special suitability for construction sites, usually for gas and water pipelines, the arc welding with stick electrode according to EN 499 [HDD-361] is used (cf. also DVGW GW 350 [HDD-362]). In pipeline construction, in this regard, stick electrodes that are wrapped with cellulose and are welded together vertically, have … |

|
The welding seams created at the construction site must be tested for defects and cracks in a non-destructive manner. Besides the test seams, for the construction site area only non-destructive tests come into question and in particular (Table 66) [HDD-330]: -
visual inspection,
-
liquid penetration test,
-
ultrasonic inspection,
-
radiographic inspection.
Type and extent of the non-destructive testing need to be arranged with experts especially for high-… |
|
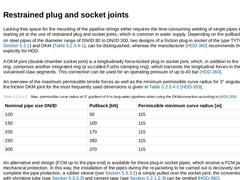
Lacking free space for the mounting of the pipeline strings either requires the time-consuming welding of single pipes inside the starting pit or the use of restrained plug and socket joints, which is common in water supply. Depending on the pullback force applied on steel pipes of the diameter range of DN/ID 80 to DN/ID 300, two designs of a friction plug-in socket of the type TYTON®- SIT (see (Joints of ductile cast iron pipes)) and DKM (Table … |

|
Considering the pressure levels that can be achieved, the operating conditions and the fluid transported, the pipe material steel offers a wide range of connection techniques, especially butt-welded joints or welded sockets or spigot joints [HDD-359]. Due to their absolute axial restraint, in practice only steel pipelines with butt welded joints are used for pulling-in by means of HDD. Alternatively, for water pipelines, especially in the case of … |

|
(Image: Figure 214 Preferable external diameter and wall thicknesses for steel pipes according to DIN EN 10208-1 (marked by the framed field including frame))The construction length of steel pipes usually ranges between 6 m and 18 m [HDD-360]. Depending on the wall thickness and the type of pipe joint, for gas and water pipes, the maximum operating pressures that are required and given in the corresponding manufacturing standards can be applied. … |

|
Steels are the most frequently used metallic materials for manufacturing pipes. According to the classic definition, steel is an alloy that consists of iron and carbon and that contains less than 2.06% (mass) carbon. EN 10020 [HDD-301] also follows this definition, according to which steels are materials whose mass proportion of iron is greater than that of any other element, whose carbon concentration is generally smaller than 2 weight per cent.… |

|
Ductile cast iron is a ductile iron-carbon material whose carbon content predominantly consists of graphite in free form. Ductile cast iron mainly differs from the grey cast iron, which is nowadays no longer used for buried supply and discharge lines, in the shape of graphite particles [HDD-379]. Grey cast iron contains lamellar graphite, whereas ductile cast iron contains graphite spheres or spheroidal graphite. The shape of graphite mainly influences … |

|
Ductile cast iron pipes with integral joints are the conventionally used cast iron pipes that are employed for buried installation. The only exception is made for jacking pipes that do not possess a “smooth outer contour” according to the definition for jacking pipes (see (Pipe materials and joints)). Pipes of this type of construction are only suitable for pulling-in in connection with HDD or for the subsequent pulling-in into casing and host pipes … |
|
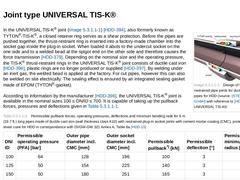
(Image: Design of flexible, tensile restrained pipe joints for ductile cast iron pipes for HDD – UNIVERSAL TIS-K®)In the UNIVERSAL TIS-K® joint (Figure 235 a) [HDD-394], also formerly known as TYTON®-TIS-K®, a closed retainer ring serves as a shear protection. Before the pipes are pushed together, the thrust-restraint ring is inserted into a factory-made chamber into the socket gap inside the plug-in socket. When loaded it abuts to the undercut socket … |

|
(Image: Design of flexible, tensile restrained pipe joints for ductile cast iron pipes for HDD – BLS® (DN/ID 80 to 500))The method of functioning of the BLS®/VRS®-T-joint [HDD-394] [HDD-395], formerly also known as TYTON®-TKF, is similar to the UNIVERSAL TIS-K® joint (see (Joint type UNIVERSAL TIS-K®)). In place of the closed retainer ring, several retainer segments are used, that however are pushed into the retainer chamber through windows in the … |

|
Ductile cast iron pipes with integral joints are the conventionally used cast iron pipes that are employed for buried installation. The only exception is made for jacking pipes that do not possess a “smooth outer contour” according to the definition for jacking pipes (see (Pipe materials and joints)). Pipes of this type of construction are only suitable for pulling-in in connection with HDD or for the subsequent pulling-in into casing and host pipes … |

|
On ductile cast iron pipes for water supply pipelines with allowable maximum operating pressures (PFA) according to DIN EN 545 [HDD-382], welding by electric arc welding can be carried out by means of special nickel- iron electrodes [HDD-395]: -
welding of sockets made of ductile cast iron or steel DN 2",
-
welding of outlets made of ductile cast iron or steel DN 80 to DN 300,
-
wall flanges for integration into constructions,
-
manufacturing flanged …
|

|
At the factory, ductile cast iron pipes for use in buried applications are protected against external attack by aggressive soils [HDD-404] and or filling materials with suitable protective coatings according to DIN EN 545 [HDD-382]. The following variants are to be considered as external protection [HDD-396]: -
zinc coating with bitumen cover coating according to DIN 30674-3 [HDD-405],
-
zinc-aluminium coating with cover coating made of epoxy or polyurethane (…
|

|
Ductile cast iron pipes must be installed in such way that the external protection is not damaged. Due to the socket design, the pipe joint represents a particularly sensitive area in this connection. DVGW GW 321 [HDD-15] stipulates that, for the joint areas, heat-shrinking sleeves (shrinking material) according to DIN 30672 [HDD-333] (see (Pipe joints)) or rubber sleeves should be used as suitable external joint protection. In all cases, these external … |

|
|
|
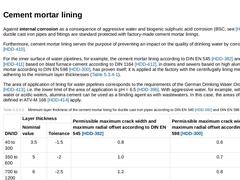
Against internal corrosion as a consequence of aggressive water and biogenic sulphuric acid corrosion (BSC, see [HDD-43]), ductile cast iron pipes and fittings are standard protected with factory-made cement mortar linings. Furthermore, cement mortar lining serves the purpose of preventing an impact on the quality of drinking water by corrosion products [HDD-410]. For the inner surface of water pipelines, for example, the cement mortar lining according … |

|
Ductile cast iron is a ductile iron-carbon material whose carbon content predominantly consists of graphite in free form. Ductile cast iron mainly differs from the grey cast iron, which is nowadays no longer used for buried supply and discharge lines, in the shape of graphite particles [HDD-379]. Grey cast iron contains lamellar graphite, whereas ductile cast iron contains graphite spheres or spheroidal graphite. The shape of graphite mainly influences … |

|
Polyethylene (PE) belongs to the group of semi-crystalline thermoplastics (polyolefin). It is marked by a high degree of flexibility and ductility also at low temperatures [HDD-415] [HDD-416]. PE is resistant to acids, alkalis and weak solvents. It is not resistant to oxidising acids and halogens. Further information in this respect is contained in the Addendum to DIN 8075 [HDD-417]. For PE-pipes, which are used in HDD, the following standards apply: |

|
For the connection of PE-pipes, generally the following welding techniques can be used: -
heated coil socket welding,
-
extrusion welding,
-
heated tool or butt fusion welding.
In heated coil socket welding, electric welding fittings with integrated resistance wires are used for creating a pipe joint. They are electrically charged during welding (Figure 238). Pulling-in the pipe string that is welded by means of heated coil sockets without causing destruction … |

|
According to DVGW GW 321 [HDD-15] with reference to DVS 2207-1 [HDD-435] and/or ASTM D3261-03 [HDD-436] and ASTM D2657-03 [HDD-437], PE 80 and PE 100-pipes for use in HDD must be connected by heated tool or butt fusion welding (Figure 240) [HDD-438]. In this welding technique, the connection surfaces of the pipes to be welded are heated under pressure at the heating element and are connected after removing the heating element (Figure 239 and Figure … |

|
The following devices and materials are necessary for heated tool or butt fusion welding (Figure 241) [HDD-439] [HDD-440]: -
welding slide,
-
hydraulic power unit,
-
insertion shoulders for different pipe diameters,
-
facer,
-
heating element with control unit,
-
cleaning tissues and ethyl alcohol,
-
data recording device with outside temperature sensor, pressure sensor, etc.
For heated tool or butt fusion welding, only trained staff with a valid welder … |

|
The following preparatory works must be completed before starting the welding: -
checking the roundness of the pipes and adjusting if necessary,
-
clamping the pipe ends axially into the welding slide,
-
pipe ends are “faced” with a machining tool to establish clean, parallel mating surfaces, perpendicular to the centreline of each pipe,
-
checking the plane parallelism and displaced joints and adjusting, if necessary,
-
cleaning the heating element,
-
…
|

|
The following working steps are necessary: -
adjusting (Figure 242a),
-
heating (Figure 242b),
-
relocating (Figure 242c),
-
joining (Figure 242d).
The pressures and times that must be observed for the welding process must be taken from the information by the manufacturer (see e.g. Table 79). (Table: Table 79: Guideline values for heated tool or butt fusion welding of PE-pipes and fittings at an atmospheric temperature of around 20 °C (68°F) and moderate … |

|
(Image: Working steps for PE-welding with corresponding temperature diagram – Joining)Welding works must be monitored. The type and extent must be arranged between the contract partners. It is recommended to document the process data in welding protocols or on data storage media [HDD-435] [HDD-441]. The welding protocol must contain the following data (cf. also diagram in Figure 242 d): -
melting temperature,
-
melting time,
-
jointing pressure.
|

|
The developing outer and inner welding seams, also called welding beads, are removed with corresponding devices (Figure 243a and b), where required. (Image: Testing the welding seam by means of nondestructive ultrasonic inspection using the example of detecting a lack of fusion in the joint gap section – Sketch) (Image: Testing the welding seam by means of nondestructive ultrasonic inspection using the example of detecting a lack of fusion in the … |