
|

|

|

|
(Image: Conctrete sewer with defective branch connection and corrosion)
|
|
(Image: Corrosion of bricks [Frank92])
|
Especially for sewage installations, [ATVM168] defines corrosion as follows: "Under corrosion in the field of sewage installations there are understood to be all reactions to non-metallic and metallic construction and other materials with their environment which, due to chemical, electro-chemical and microbiological processes, lead to … |
|
|

|
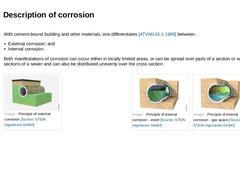
With cement-bound building and other materials, one differentiates [ATVM143-1:1989] between: - External corrosion; and
- Internal corrosion.
Both manifestations of corrosion can occur either in locally limited areas, or can be spread over parts of a section or whole sections of a sewer and can also be distributed unevenly over the cross section . | | (Image: Principle of external corrosion)
| |
(Image: Principle of internal corrosion - invert)
|
(Image: Principle … |
|
|

|

|
According to [ATVM143-1:1989], internal corrosion can have the following causes: - Non adherence to standards and regulations, e.g. EN 1610 [DINEN1610:1997], ATV-A 115E [ATVA115b], EN 752 [DINEN752-1a].
- Non adherence to the limiting values of standards and guidelines (e.g. DIN 4030 [DIN4030:1991] for concrete or cement-bound materials).
- Formation of aggressive sewage due to the influx of various substances (chemical processes), influences also due …
|
|

|

|
Whilst only the wetted sewer region is affected by the corrosion resulting from the direct effect of aggressive sewage, the effects of biogenic sulphuric acid corrosion, that is, the microbiological processes, will only be found in the gas space, i.e. above the water level . |
(Image: Principle of sequence of bionic sulphuric acid corrosion with reference to [Bock84] [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
(Image: Biogenic sulphuric acid corrosion in a manhole [FI-Hermea])
|
|
|

|

|
The possible consequences of damage resulting from corrosion depend substantially on the type of corrosion, its manifestation and extent and, according to [ATVM143-1:1989] are - Leakiness
- Reduction of the wall thickness and thus its accompanying reduction of bearing strength with the possible consequential damage of cracks, deformation, pipe break, collapse.
(Image: Sequence of partly collapsed masonry sewer resulting from corrosion of the jointing … |
|

|

|
|

|
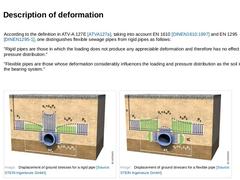
According to the definition in ATV-A 127E [ATVA127a], taking into account EN 1610 [DINEN1610:1997] and EN 1295 [DINEN1295-1], one distinguishes flexible sewage pipes from rigid pipes as follows: "Rigid pipes are those in which the loading does not produce any appreciable deformation and therefore has no effect on pressure distribution." "Flexible pipes are those whose deformation considerably influences the loading and pressure distribution as the … |
|

|

|
Deformations in the sense of damage can be caused by [ATVM143-1:1989] : - Non adherence to the standards and regulations (e.g. EN 1610 [DINEN1610:1997] or ATV-A 127 [ATVA127a]), for instance by:
- Missing or incorrect statics calculations;
- Laying of unsuitable or defective pipes;
- Deviating from the load and/or support conditions of the calculation assumptions [ATVA241:1994] ;
- Unprofessional laying and/or bedding, poor annulus grouting with a trenchless …
|
|

|

|
The possible consequences of damage of deformation are, according to [ATVM143-1:1989] : - Reduction of the hydraulic effectiveness;
- Blockages;
- Increase of the maintenance effort;
- Crack danger for form pieces at those points that, due to formed branches, kinks, etc. are stiffer than the unstiffened pipe;
- The danger of bulges with very large deformations;
- Tension crack deformation;
- Leaks;
- Cracks;
- Pipe break;
- Collapse.
|
|

|

|

|

|
The "cracks" type of damage occurs primarily in rigid piping, whereby distinction is made between three main forms which can be the precursors for the pipe break and, finally, for the collapse of the sewer [ATVM143-1:1989]. - Longitudinal cracks;
- Lateral cracks;
- Cracks originating at a point (in some cases also with pipe fracture).
Of the main forms of cracks mentioned, the ones that occur most often in rigid piping are longitudinal cracks . In most … |
|

|

| (Image: Storage of concrete pipes on site)
Irrespective of the type of crack, the following are mentioned as causes [ATVM143-1:1989] : - Non-adherence to the standards and regulations, e.g. EN 1610 [DINEN1610:1997], ATV-A 127E [ATVA127a].
- Damage to the pipes during transport, storage, laying, bedding, backfilling or compacting.
- Effects of wear.
|
|
|

|
Besides the causes of damage already mentioned above, longitudinal cracks occur specially through (not found): -
The lay of the pipes.
-
As a result of leakiness, position deviation, mechanical wear, corrosion or deformation.
|
(Image: Longitudinal cracks in rigid pipes with reference to [Young84] [Image: S&P GmbH]) |
|
(Video: Development of a longitudinal crack as a result of a leak in a pipe joint with infiltration of groundwater and soil with reference … |
|
|

|
(Image: Formation of circumferential cracks due to incorrect support of the pipe with reference to [Brenn76] [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
|
(Image: Circumferential crack about the whole circumference [FI-KMG])
|
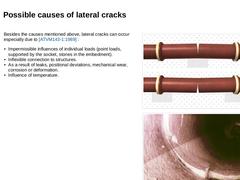
Besides the causes mentioned above, lateral cracks can occur especially due to [ATVM143-1:1989] : - Impermissible influences of individual loads (point loads, supported by the socket, stones in the embedment).
- Inflexible connection to structures.
- As a …
|
|

|

|
(Image: Cracks orginating at a point with reference to [Young84] [Image: S&P GmbH])
|
|
(Image: Fragmentation of a vitrified clay pipe)
|
The most important causes of damage for cracks originating at a point which can lead to pipe fracture, besides those mentioned above, are: - Impermissible influences of individual loads (point loads, supported by the socket, stones in the embedment).
- Incorrect connections of the lateral due to caulking the sewer.
- Extreme …
|
|

|

|
All shapes of cracks, with the exception of the lateral cracks, carry with them a priori the danger of loss of stability, whereby the time of total failure (collapse) depends on some of the influencing factors mentioned above and can therefore not be predicted with accuracy [Flatt83] [Trott80]. Under advantageous conditions, e.g. small width of crack, no groundwater, good bedding, constant operating conditions (no overloading / flooding), a pipe … |
|

|

|

|

|
Pipe break is understood to be the missing of more or less large pieces of the pipe walling . Collapse is understood to be the complete loss of carrying capacity connected with the destruction of the respective component . |
(Image: Pipe break - a piece of wall is missing [FI-IfK])
|
(Image: Collapse - concrete sewer [FI-KMG])
|
|
|

|

|
A pipe break is caused by an additional malfunction or changed internal or external loading of an already damaged pipe having a crack or being fractured. Furthermore, according to [ATVM143-1:1989], it occurs due to leaks, mechanical wear, corrosion and cracks. A collapse is the final phase, and the one with the most serious consequences, in the development of the following damage over a period of time. - Leakiness .
- Mechanical wear .
- Corrosion .
- Deformation .
|
|

|

|
All cracks that have penetrated through the pipe, thus also the lateral cracks and pipe breaks, are a priori points of leaks with the consequences as mentioned in . Due to the in- or exfiltration connected with this, the bedding conditions of the affected pipe region are changed so that position deviations connected with new formation of cracks or further deformation of the cracked pipe up to collapse can occur . The fragments that have fallen into … |
|

|

|

|

The aim of this lecture is to provide an overview of the main damage groups, its causes and its consequences. |

|

|
The successful application of the individual processes depends on the degree of moisture and the degree of contamination of the cracks. In [DAfStBb] [Verkehra], four conditions of moisture are defined in greater detail as: - "dry",
- "moist"
- "water flow without pressure and
- "water flow under pressure" .
| |
(Image: Crack - dry)
|
(Image: Crack - moist)
|
(Image: Crack – water-bearing without pressure)
|
(Image: Crack – water-bearing under pressure [FI-Winkl])
|
|
|

|

(Table: Distribution of the moisture conditions of cracks/crack edges in accordance with [Verkehra]) |
|