
|
In recognition of these facts for new sewer installations laterals are to be connected simultaneously with the construction of the sewer, whereby all connection types without branches are only permitted to be built by means of fittings and sealing elements which are standardised or have a valid test report. The inlet angle shall be 45°. For nominal sizes of the sewer ≥ DN 500 or a diameter ratio of about 1 : 3 between the connection- and sewer connections … |

|
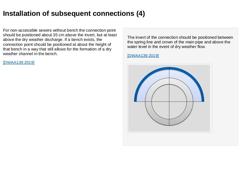
For non-accessible sewers up to DN 800, the connection point should preferably be placed between the spring line and crown of the main pipe. (Image: Examples of the jointing of connecting drains into the street sewer with reference to [ATVA139b] - Angled connection with small height difference [Image: S&P GmbH]) (Image: Examples of the jointing of connecting drains into the street sewer with reference to [ATVA139b] - Angled connection with small height … |
|
For non-accessible sewers without bench the connection point should be positioned about 35 cm above the invert, but at least above the dry weather discharge. If a bench exists, the connection point should be positioned at about the height of that bench in a way that still allows for the formation of a dry weather channel in the bench. [DWAA139:2019] The invert of the connection should be positioned between the spring line and crown of the main pipe … |

|
As a basic principle, connections must always be made in order to ensure that they can absorb movements. The planner has to define the type and constructional design of the connections by taking into consideration both possible settlements and resulting loads in the connection area. [DWAA139:2019] (Image: Faulty connection - lateral connection projects beyond the inner surface of the existing pipe) In this respect, DIN EN 1610 stipulates that connections … |

|
DIN EN 1610 provides the following connection variants: -
Connections to the sewer
-
Branches,
-
Connecting fittings (sealing media offset back from the inner wall of the core boring thus created),
-
Saddle fittings (sealing medium between the outer surface of existing pipes and the inner surface of the saddle flange),
-
Welding
-
Connections to manholes and inspection chambers.
[EN1610:2015] |

|
The images illustrate some examples for connections to sewers of concrete or reinforced concrete, ductile cast iron, vitrified clay and plastics by means of branches, connecting fittings or saddle fittings. The results of an analysis that has been made in order to assess and test different connection variants can be found in [Stein96h]. (Image: Examples for connections – Saddle fitting of ductile cast iron) (Image: Screwable saddle fitting of GRP) (… |

|
Connecting fittings, saddle fittings and the connection achieved by welding require one connection opening each that is to be made subsequently, i.e. after the pipe is manufactured or laid, by means of a suitable core drilling machine. The tools and methods which are needed for that purpose “have to be chosen and applied in accordance with the system. Reinforcing steel must be protected against corrosion. The permanent leaktightness of the connection … |

|
The way of connecting drains and laterals to sewers which has its origin in the 19th century at the beginning of modern sewerage technology has always been recognised as weakness of the system that resulted in the following facts: -
Especially in the intra-urban area, the concentration of connections can be quite dense, whereby distances between inlets of 1 to 2 m are not uncommon,
-
Subsequently made connections to non-accessible …
|
|
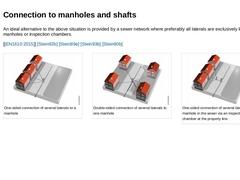
An ideal alternative to the above situation is provided by a sewer network where preferably all laterals are exclusively led into manholes or inspection chambers. [ [EN1610:2015]] [Stein92b] [Stein89e] [Stein93b] [Stein80b] (Image: Connection variant of laterals to manholes) (Image: Connection variant of laterals to manholes) (Image: Connection variant of laterals to manholes) |

|
An example for a manhole with several connections is illustrated in Image. This solution has been implemented, for example, under the designation “Berlin structure” in the trenchless method of sewer construction. [Stein80b] [Möhri94] [Möhri93b] [Möhri93a] In this method, connections to the sewer section are foregone by an extension of the anyway required starting- and target pits for the radial jacking of the laterals in any height and direction. [Stein03] [… |

|
Instead of the connections with vertically arranged laterals, the connections can also be combined with a circumferential gutter that is arranged along the inner contour of the manhole in order to improve hydraulics. (Video: Sewer connection manhole with circumferential gutter with reference to [Ullma94] [Image: S&P GmbH]) Video: Sewer connection manhole with circumferential gutter with reference to [Ullma94] [Image: S&P GmbH]. This interactive object … |

|
Advantages: This indirect linkage of the drains and laterals to the sewer has the following advantages: -
Easier maintenance and inspection,
-
Easier elimination of damage both in the laterals and in the sewer,
-
Ability to monitor the sewage discharged from a private property at any time.
[Stein03] [Stein84e] [Möhri87b] This fully meets the requirement for installations that are easy to maintain as well as the maintainability requirement of DIN EN 752. … |

|
|
|
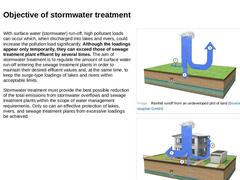
With surface water (stormwater) run-off, high pollutant loads can occur which, when discharged into lakes and rivers, could increase the pollution load significantly. Although the loadings appear only temporarily, they can exceed those of sewage treatment plant effluent by several times. The aim of stormwater treatment is to regulate the amount of surface water run-off entering the sewage treatment plants in order to maintain their desired effluent … |

|
The term “stormwater facilities" includes the buildings of the central stormwater treatment and stormwater detention. Stormwater facilities are an effective way of reducing peak flow and equalising flow rates from storm water runoffs in the sewer system. Placed strategically, stormwater facilities mean better utilisation of the existing sewer system, allow for intelligent management of storm water flows, and ultimately save on infrastructure investments. |
|
First flush In the first minutes of a storm water runoff event, a batch of water termed the first flush will arrive. The first flush carries high concentrations of organic and inorganic matter to the wastewater treatment plant respectively to the stormwater facilities. This material has accumulated in the sewer system,or on the drained area, during periods without rain. Absorbed in this material are various chemicals such as heavy metals and xenobiotics. … |

|
Retention time Retention time of the stored wastewater is controlled by available space in the sewer system, and this determines when wastewater from the stormwater facilities can be conveyed back. This can normally be done immediately after the stormwater runoff event and the tank can be empty within 24-48 hours after the first inflow. During extended periods of detention, unintended issues such as odour problems might arise, resulting from the combination … |
|
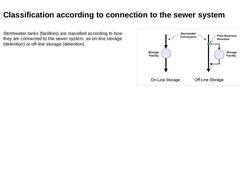
Stormwater tanks (facilities) are classified according to how they are connected to the sewer system, as on-line storage (detention) or off-line storage (detention). (Image: On-Line versus Off-Line Storage) |
|
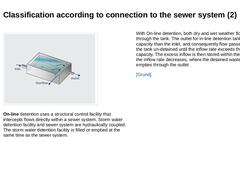
(Image: On-line storage) On-line detention uses a structural control facility that intercepts flows directly within a sewer system. Storm water detention facility and sewer system are hydraulically coupled. The storm water detention facility is filled or emptied at the same time as the sewer system. With On-line detention, both dry and wet weather flow passes through the tank. The outlet for in-line detention tanks has less capacity than the inlet, … |
|
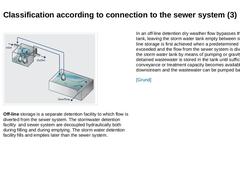
(Image: Off-line storage) Off-line storage is a separate detention facility to which flow is diverted from the sewer system. The stormwater detention facility and sewer system are decoupled hydraulically both during filling and during emptying. The storm water detention facility fills and empties later than the sewer system. In an off-line detention dry weather flow bypasses the storage tank, leaving the storm water tank empty between storms. Off-line … |

|
Static operation mode: constant adjustment of water levels and outflows Managed operation mode: variable adjustment of water levels and outflows |

|
For water management and cost reasons the priority task of the wastewater collection measures planning and stormwater treatment is the avoidance of stormwater overflow into the sewer system whenever possible. For the remaining discharges, for technical water management and economic reasons, stormwater structures with overflows are located in combined wastewater sewers. Combined sewer systems structures with overflows into lakes or rivers include: |
|
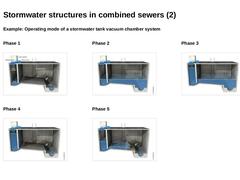
Example: Operating mode of a stormwater tank vacuum chamber system Phase 1 (Image: Flushing chamber schematic - initial stage (Biogest-System)) Phase 2 (Image: Retention phase of a vacuum stormwater tank system (Biogest-System)) Phase 3 (Image: Retention phase of a vacuum stormwater tank system (Biogest-System)) Phase 4 (Image: Retention phase of a vacuum stormwater tank system (Biogest-System)) Phase 5 (Image: Flushing chamber schematic - release of the flushing … |

|
Separate drainage method/separate system -
Stormwater detention tank/basins
-
Stormwater purification tank/basin
-
Retention basin (soil filter) unit
(Image: Drainage of wastewater and surface water in separate system) |

|
Stormwater tank retaining the first flush of stormwater These stormwater tanks have the exclusive task of combined wastewater storage. A sedimentation of settleable solids should be made more difficult with regard to trouble-free cleaning and avoidable intermittent loading of the wastewater treatment plant through appropriate design measures or mechanical equipment“. Stormwater tanks with overflow have, next to the combined wastewater storage, the … |