
|

Beim unsachgemäßen Einsatz der Hochdruckreinigung können die Druckwasserstrahlen Schäden in Form von Riefen, Abplatzungen, Rissen oder Löchern in Rohrwandungen und Rohrauskleidungen erzeugen. |
(Bild: Schaden durch unsachgemäß eingesetztes HD-Spülverfahren [Prüfattest]) |
(Bild: Schaden durch unsachgemäß eingesetztes HD-Spülverfahren [Prüfattest]) |
Bilder: Schaden in einem Steinzeugrohr durch unsachgemäß eingesetzte Hochdruckreinigung [Züric1987] |

|

Besondere Gefahrenmomente für den Abwasserkanal ergeben sich darüber hinaus aus dem Schlagen der Reinigungsdüse, dem Aufwirbeln von gelösten Ablagerungen bzw. Geschiebepartikeln und beim Verharren der Reinigungsdüse unter Last an einer Stelle. (Bild: Schlagende Düse 1) |

|

Die Belastungen der Rohroberfläche werden durch folgende Einflussfaktoren bestimmt: -
Düsentyp
-
Düsengewicht
-
Wasserdruck an der Düse
-
Wasser-Volumenstrom
-
Abstand der Düse zur Rohrwandung
-
Anzahl, Querschnitt und Strahlwinkel der Düsenbohrungen bzw. -einsätze
-
Vorschub- und Rückzuggeschwindigkeit der Düse
-
Reinigungshäufigkeit
|

|

(Bild: Schaden durch Hochdruckreinigung im Kanal) Kanal -
Werkstoff (duktil, spröde, Druck-, Zug-, Sprödbruchfestigkeit)
-
Nennweite
-
Wanddicke
-
Qualität der Bettung
-
Baulicher Zustand
(Bild: Strahlumlenkung in der Düse) Düse -
Düsentyp
-
Düsengewicht
-
Anzahl und Durchmesser der Düsenöffnungen
-
Art der Düseneinsätze
-
Strahlumlenkung in der Düse
(Bild: Spül Saugfahrzeug Stadt Bochum) Reinigung -
Düseneinlass- und Rückzugsgeschwindigkeit
-
Anzahl der Reinigungszyklen
|

|

|

|

Seit den 80er Jahren des 20. Jahrhunderts bemüht man sich, Prüfverfahren zur Ermittlung der Beständigkeit von Rohren, Formstücken und Rohrverbindungen für Abwasserleitungen und -kanäle gegenüber den Beanspruchungen bei der Hochdruckreinigung zu entwickeln. Dieser Prozess ist mit der seit 08/2008 gültigen Norm DIN 19523 „Anforderungen und Prüfverfahren zur Ermittlung der Hochdruckstrahlbeständigkeit und -spülfestigkeit von Rohrleitungsteilen für Abwasserleitungen … |

|

Die Prüfungen nach DIN 19523 beinhalten: -
Werkstoffprüfung
-
Praxisprüfung
Die hydraulischen Belastungen durch den Spülstrahl werden durch die Werkstoffprüfung abgebildet; die hydraulischen und mechanischen Einwirkungen, die bei einer Hochdruckreinigung auftreten, werden durch die Praxisprüfung simuliert. |

|

Bei der Werkstoffprüfung wird eine Prüfstrecke mit einer Länge von 1,0 m mit einem Druckwasserstrahl belastet, der unter einem Winkel von 30° und mit einem vertikalen Abstand zwischen Prüfoberfläche und Mitte Düseneinsatz von 10 mm auf die Oberfläche des Bauteils trifft. Die Mindestlänge des zu prüfenden Bauteiles sollte dabei 1,30 m betragen. Geprüft werden drei Prüfstrecken, die in einem seitlichen Abstand von mindestens 10 cm zueinander liegen. … |

|

Bei der Praxisprüfung werden die Belastungen bei der Hochdruckreinigung simuliert, die durch die Druckwasserstrahlen in Kombination mit den mechanischen Belastungen durch Spülkopf und Schlauch verursacht werden. (Bild: Untersuchung des Einflusses der HD-Spülung auf Einbindungen von Anschlußleitungen [Stein96h]) (Bild: Untersuchung des Einflusses der Hochdruckreinigung auf Kunststoffrohre) |

|

|

|

Reinigungsdüsen sind so einzusetzen, dass ein Umkehren in der Haltung vermieden wird. Diese Forderung wird eingehalten, wenn eine im Verhältnis zum Kanal richtig dimensionierte Reinigungsdüse eingesetzt und durch Verwendung eines Drehgelenks zwischen dieser und dem Spülschlauch eine Verdrillung des Schlauches vermieden wird. Für den letztgenannten Fall kann auch eine biegesteife Verlängerung (z. B. Rohrstück) eingesetzt werden. Das Rohrstück muss … |

|

Bei der Hochdruckreinigung besteht die Gefahr der Bildung von Aerosolen, d. h. von feinst in der Luft verteilten Abwassertröpfchen, welche bei entsprechender Luftströmung über die Schächte bis zur Geländeoberfläche transportiert und für das Bedienungspersonal zur gesundheitlichen Gefahr werden können. (Bild: Starker Austritt von Aerosolen am Schacht) |

|

Der Austritt von Aerosolen aus dem Schacht kann z. B. mit Hilfe der im Bild dargestellten Gebläseeinrichtung „Aerokill“ verhindert werden. Dazu erzeugt diese Einrichtung, die durch die vorhandene Fahrzeughydraulik angetrieben wird, einen starken Luftstrom über der Rückstauebene gegen eine Filterwand. Die Aerosole sowie der Wassernebel tropfen dann an der Filterwand ab und werden in den Kanalschacht zurückgeführt. Das System ist aufgrund seiner hohen … |

|

Weitere vorbeugende Maßnahmen gegen die Bildung von Aerosolen und zum Schutz vor ihren Auswirkungen sind unter anderem: -
Einsatz von Sohlendüsen bei großen Schachtquerschnitten,
-
Reduzierung des Pumpendruckes ca. 10 m vor Erreichen des Startschachtes,
-
Verwendung von Mund- und Augenschutz und
-
Abdeckung der Schachtöffnung mit dünnem Stahlblech oder Kunststoff mit Durchführungsöffnungen für den HD-Spülschlauch und den Saugschlauch.
[ATV1997] |

|

|

|

Basierend auf Praxiserfahrungen sollten zur Sicherstellung einer fachgerechten Anwendung der Hochdruckreinigung und zur Vermeidung von Schäden folgende Hinweise und Empfehlungen beachtet werden: -
Bei der Wahl der Betriebsparameter (Düsenart, Durchfluss, Abstrahlwinkel, Druck an der Düse) sollten neben den sich aus der eigentlichen Reinigungsaufgabe ergebenden Parametern auch immer der Rohrwerkstoff, die Wanddicke und insbesondere der bauliche Zustand …
|

|

-
Der Druck an der Düse sollte bei schadensfreien Kanälen 120 bar nicht überschreiten. Der zugehörige Pumpendruck ist unter Berücksichtigung der jeweiligen Randbedingungen festzulegen und zu regulieren.
-
Bei schadhaften Kanälen muss mit einem deutlich geringeren Druck an der Düse gearbeitet werden. Dabei kann durch Erhöhung des Abstandes der Düse zur Rohrwandung, z. B. durch Verwendung einer Führungseinrichtung (Kufen oder Schlitten) die Belastung …
|

|

-
Die Reinigungsdüse darf unter keinen Umständen unter Last länger an einer Stelle verweilen, um die Entstehung bzw. Erweiterung von Schäden an Kanälen, insbesondere an den Rohrverbindungen und einragenden Seitenzuläufen, zu vermeiden.
-
Vor Beginn der Reinigungsmaßnahme ist zu überprüfen, ob die Düsenöffnungen verstopft sind, um zusätzliche und unkontrollierte Reaktionskräfte an der Düse und damit verstärkte Beanspruchungen der Rohrwandungen zu vermeiden.
|

|

-
Bei Temperaturen < 0° C sind die Reinigungsfahrzeuge mit Frostschutzverkleidungen zu versehen, um das Zufrieren von Pumpen und Leitungen zu verhindern. Die Verkleidungen können auch Lärmschutzfunktionen übernehmen.
-
Kunststoffschläuche sind aufgrund ihrer besseren hydraulischen Eigenschaften und aus Gewichtsgründen den Gummischläuchen vorzuziehen. Allerdings sollten die ersten 10 bis 20 m aus Gummischlauch ausgeführt werden, da dieser flexibler …
|

|

Bei der Hochdruckreinigung treten außerdem oftmals starke Luftströmungen auf. Diese Wechselwirkung erzeugt einen mehr oder weniger großen Drucksprung an der Düse, d. h. vor der Düse entsteht ein Unterdruck (Düsenkopf) und hinter der Düse (Strahlbereich) ein Überdruck. Beim Passieren der Reinigungsdüse an Seitenzuläufen (Hausanschlüssen), kann es dadurch zu Ausblasungen bzw. zur Absaugung von Sperrwasser aus Geruchsverschlüssen der Hausinstallationen (… |

|

Folgende Maßnahmen können die Gefahren der Geruchsbelästigungen minimieren: -
Reduzierung des Pumpendruckes am Fahrzeug (damit auch kleinerer Spüldruck)
-
Auswahl der richtigen Reinigungsdüse (große Strahlwinkel, geringe Anzahl von Düseneinsätzen)
-
Reduzierung der Rückzuggeschwindigkeit der Düse
-
Reinigung möglichst kurzer Abschnitte von Schacht zu Schacht,
-
regelmäßiges Entfernen des Räumgutes innerhalb einer Haltung und
-
Verbesserung der Luftzufuhr …
|
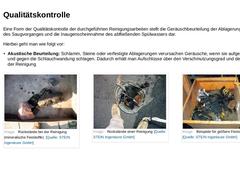
|

Eine Form der Qualitätskontrolle der durchgeführten Reinigungsarbeiten stellt die Geräuschbeurteilung der Ablagerungen während des Saugvorganges und die Inaugenscheinnahme des abfließenden Spülwassers dar. Hierbei geht man wie folgt vor: -
Akustische Beurteilung: Schlamm, Steine oder verfestigte Ablagerungen verursachen Geräusche, wenn sie aufgesaugt werden und gegen die Schlauchwandung schlagen. Dadurch erhält man Aufschlüsse über den Verschmutzungsgrad …
|

|

Visuelle Beurteilung: Durch Inaugenscheinnahme der Beschaffenheit bzw. Färbung des abfließenden Spülwassers lassen sich Rückschlüsse auf die Reinigungsergebnisse ziehen. (Bild: Kontrolle der Reinigungsarbeit) (Bild: Schacht Reinigung Kontrolle) Weitere Leistungsindikatoren für die Beurteilung der Reinigungsarbeit sind in DIN EN 14654-1 enthalten. |

|

|

|

(Bild: Radialdüse Querschnitt) Düse:
- Anzahl und Durchmesser der Düsenöffnungen - Art der Düseneinsätze - Strahlumlenkung in der Düse (Druckverluste) (Bild: Ablagerungen Abwasserkanal-Mischungen aus organischen und mineralischen Stoffen) Kanal (Reinigungsziel):
- Nennweite, Länge,Tiefenlage - Werkstoff - Baulicher Zustand - Menge und Beschaffenheit der An- und Ablagerungen - Füllungsgrad, Strömungsverhältnisse (Bild: Spül Saugfahrzeug Stadt Bochum) Fahrzeug… |