
|

Für die Reinigung von Kanälen mit ständig hohen Füllungsgraden und nicht verfestigten Ablagerungen wurde im Auftrag der Emschergenossenschaft (Essen) vom Fraunhofer-Institut für Fabrikbetrieb und ‑automatisierung IFF (Magdeburg) ein automatisches Reinigungssystem für Großprofile entwickelt, welches gleichzeitig für eine detaillierte Inspektion genutzt werden kann. |

|

Das Reinigungs- und Inspektionssystem mit der Bezeichnung SVM-RS ist mit einem variablen, allradgetriebenen Fahrwerk ausgestattet, welches die Fortbewegung und exakte Positionierung entlang des Kanals in teilgefüllten Kanälen ermöglicht. Durch die einfache Adaption des Fahrwerks kann das SVM-RS vielseitig in Haltungen mit Nennweiten von DN 1600 bis DN 2800 und Längen bis 1200 m eingesetzt werden [Saenz2010] [Saenz2010a]. (Bild: Einsatzszenario des … |

|

Herzlichen Glückwunsch! Hiermit haben Sie die vorliegende Lektion erfolgreich beendet. Im Anschluss haben Sie nun die Möglichkeit, das neu erlangte Wissen mithilfe eines interaktiven Fragebogens selbstverantwortlich zu überprüfen. Natürlich können Sie außerdem nach wie vor zu einem beliebigen Punkt in den vergangenen Lektionen zurücknavigieren, um das eine oder andere Thema oder Detail erneut anzuschauen. Bleiben Sie neugierig! |

|

Die Reinigung von Großprofilen stellt die Fachkräfte vor besondere Herausforderungen. Diese Lektion beschäftigt sich daher ausschließlich mit diesem Thema. Im Mittelpunkt der Lektion steht unter anderem die Darstellung von Maschinen, die speziell für diesen Einsatzzweck konzipiert wurden. Nach Abschluss der Lektion verfügen Sie über Kenntnisse bezüglich: - Verfahren zur Reinigung von Großprofilen;
- Rahmenbedingungen für ein Großprofil-Reinigung.
|

|

Bei der Reinigung von Druckleitungen, d. h. von „Leitungen zum Transport von Abwasser unter Druck“, kommen zum Einsatz.
|

|

Physikalische Verfahren zielen in diesem Anwendungsfall darauf ab, die Fließgeschwindigkeit des Abwassers für Reinigungszwecke durch Zugabe von Luft zu erhöhen. |

|

Bei der Reinigung mit mechanischen Verfahren finden die aus dem Gas- und Wassersektor sowie der Pipelinetechnik bekannten Molche Anwendung [Führb1980] [Arsco1979] [Jenki1968] [Jordan] [Walsk1984]. |

|

Der Molch verschließt den Leitungsquerschnitt und wird entweder vom Transportmedium durch die zu reinigende Leitung gedrückt oder muss durch extra aufgewendeten Druck (Wasser oder Druckluft) durch die Leitung gepresst werden. Das Einsetzen des Molches in die Druckleitung bzw. dessen Entnahme erfolgt durch Schleusen (Molch-Fallen). Hierfür werden Armaturen, wie Kugelhähne und Absperrschieber benötigt, die den Leitungsquerschnitt vollständig öffnen.… |

|

Nach DIN EN 752 versteht man unter einem Düker einen „Abschnitt einer Freispiegelleitung oder eines Freispiegelkanals, welcher tiefer als die oben- und untenliegenden Abschnitte angeordnet ist, damit ein Hindernis unterfahren werden kann, und der daher unter Druck betrieben wird“. Düker sind insbesondere dann, wenn sie zur Ableitung von Misch- oder Niederschlagswasser dienen im Allgemeinen nicht an- und ablagerungsfrei zu betreiben [Loren2003], da … |

|

Zur Vermeidung oder Entfernung dieser An- und Ablagerungen dienen: - Hochdruckreinigung auch unter Verwendung von Ejektordüsen
- Molchverfahren
Darüber hinaus besteht die Möglichkeit, die Fließgeschwindigkeit durch konstruktive Maßnahmen zu beeinflussen:
- Spülpumpensystem
- Luftkissendüker
|
|

Das Prinzip des Spülpumpensystems basiert auf der regelmäßigen Fließgeschwindigkeitserhöhung zur Mobilisierung von Ablagerungen. Gemäß dem Gesetz der kommunizierenden Röhren ist für einen Düker innerhalb einer Freispiegelleitung der Wasserspiegel auf der linken und rechten Seite gleich. Die dazugehörige Druck- bzw. Energielinie verläuft horizontal (ohne Durchströmung). (Video: Spülpumpensystem - Düker) Video: Spülpumpensystem - Düker [Bild: Prof. … |

|

Der Luftkissendüker [DWAA112:2007] unterscheidet sich von einem konventionellen Düker dahingehend, dass der Abflussquerschnitt der Dükerleitung (Füllhöhe bzw. Teilfüllungsgrad) durch ein sogenanntes Luftkissen reduziert und damit die Fließgeschwindigkeit erhöht werden kann [Hosan1998]. Dieses Luftkissen entsteht durch kontrolliertes Einleiten von Luft in die Dükerleitung. Damit die eingeleitete Luft nicht wieder entweichen kann, ist jeweils im Ein- … |

|

Die Hochdruckreinigung ist das derzeit überwiegend angewandte Verfahren zur Reinigung von Abwasserkanälen. Nach einer Umfrage von Stein aus dem Jahr 2000 [SteinD00a] lag die Anwendung der Hochdruckreinigung in Nordrhein-Westfalen (NRW) bei über 95 % und bundesweit bei rund 90 % [Geib2002]. Der prozentuale Anteil der anderen Reinigungsverfahren liegt demnach in Deutschland bei höchstens 10 %. |

|

(Tabelle: Empfohlene Einsatzbereiche für Reinigungsverfahren) |

|

Herzlichen Glückwunsch! Hiermit haben Sie die vorliegende Lektion erfolgreich beendet. Im Anschluss haben Sie nun die Möglichkeit, das neu erlangte Wissen mithilfe eines interaktiven Fragebogens selbstverantwortlich zu überprüfen. Natürlich können Sie außerdem nach wie vor zu einem beliebigen Punkt in den vergangenen Lektionen zurücknavigieren, um das eine oder andere Thema oder Detail erneut anzuschauen. Bleiben Sie neugierig! |

|

Bei der Reinigung von Druckleitungen gelten besondere Rahmenbedingungen. Diese Lektion widmet sich daher explizit den Verfahren und Methoden, die bei der Reinigung dieses Leitungstyps zum Einsatz kommen. Nach Abschluss der Lektion verfügen Sie über fundierte Kenntnisse bezüglich: - Verfahren zur Reinigung von Druckleitungen und
- Verfahrensprinzipien.
|

|

Es besteht die Möglichkeit, durch konstruktive Maßnahmen die Ablagerung von Sedimenten in Kanalisationen zu reduzieren und sogar zu vermeiden. Hierfür bieten sich folgende Szenarien an: |

|

Unter semizentraler Sedimentation werden „Maßnahmen zum Feststoffrückhalt innerhalb von Kanalnetzen“ verstanden. Für diesen Zweck können Sedimentationsanlagen eingesetzt werden, wie z. B. die zur Reinigung von verschmutztem Niederschlags- und Mischwasser verwendeten Regenbecken oder der Geschiebeschacht [SteinR08].
Dabei handelt es sich um Anlagen mit einem Absetzraum, in dem die Strömungsverhältnisse es zulassen, dass Stoffe, die spezifisch schwerer … |
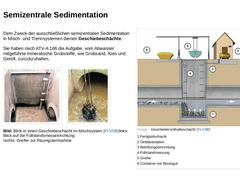
|

Dem Zweck der ausschließlichen semizentralen Sedimentation in Misch- und Trennsystemen dienen Geschiebeschächte. Sie haben nach ATV-A 166 die Aufgabe, vom Abwasser mitgeführte mineralische Grobstoffe, wie Grobsand, Kies und Geröll, zurückzuhalten. (Bild: Blick in einen Geschieberückhalteschacht [FI-VSB]) (Bild: Blick in einen Geschieberückhalteschacht [FI-VSB]) Bild: Blick in einen Geschiebeschacht im Mischsystem [FI-VSB]links: Blick auf die Füllstandsmesseinrichtung |

|

Unter dezentralem Feststoffrückhalt werden nachfolgend „Maßnahmen zum Rückhalt von Feststoffen am Ort des Anfalls vor Einleitung in die Kanalisation“ verstanden. Nach Auffassung vieler Autoren ( [Grott1991] [Giesl1997] [Kraut2000] [Stotz1998] [Somme2004a] [Somme2004] [Fraen2005] [Hilli2005] [SteinR05]) gilt der über Straßenabläufe erfolgende Regenabfluss von Bodenoberflächen als Haupteintragsquelle für mineralischen Feststoffeinträge, die wiederum … |

|

Straßenabläufe dienen zur Aufnahme des über Straßenrinnen oder -mulden zufließenden Regenwassers von Bodenoberflächen und zu dessen Ableitung über jeweils einen Anschlusskanal in den Mischwasserkanal oder in den Regenwasserkanal bei Trennsystemen. Neben der Sammlung und Ableitung des Regenwassers soll der Straßenablauf auch zum Feststoffrückhalt sowie in vielen Städten zur Belüftung der Abwasserkanäle in Mischsystemen dienen. (Bild: Straßenquerschnitt … |

|

Beim Straßenablauf mit Bodenauslauf (SB) erfolgt die Ableitung des Straßenabflusses nach Passieren des Rostes über einen mit Schlitzreihen und Löchern versehenen Eimer. Die Eimer haben die Funktion eines Siebes, das Grobstoffe und insbesondere Schwimmstoffe zurückhalten soll. Alle Partikel, die einmal die Schlitzöffnungen passiert haben, gelangen zu 100 % über den Anschlusskanal in die Kanalisation. (Bild: Straßenablauf mit Bodenauslauf (SB)) |

|

Beim Straßenablauf mit Schlammraum (SS) wird der Rückhalt von Feststoffen mit Hilfe eines Schlammraumes als Absetzraum realisiert. Dieser wird nach unten durch den Boden und nach oben durch den in die Schaftwand einmündenden Anschlusskanal begrenzt. Nachteilig bei diesem System ist, dass einerseits schwimmfähige Feststoffe, wie z. B. Laub, in der Regel direkt abgeleitet und andererseits im Schlammraum sedimentierte Feststoffe bei Starkregenereignissen … |

|

Der Feststoffrückhalt im Eimer wird maßgeblich durch den Eintrag von organischen Stoffen in Form von Laubblättern, Ästen und weiteren sperrigen Gegenständen beeinflusst. Fehlen diese im Straßenabfluss, so erfolgt praktisch kein Feststoffrückhalt, da die mineralischen Feststoffe mit Korngrößen < 16 mm die Schlitzöffnungen schon beim geringsten Volumenstrom passieren. | Daraus kann gefolgert werden, dass Straßenabläufe mit Bodenauslauf generell nicht … |
|

|

Das bedeutet, dass die derzeit gebräuchlichen Straßenabläufe nicht geeignet sind für den gezielten, geschweige denn vollständigen Rückhalt der mit dem Straßenabfluss transportierten, absetzbaren Feststoffe. Ihre Leistungsfähigkeit ist, wie Labor- und In-Situ-Untersuchungen von Stein [SteinR08] sowie die Erfahrungen vieler Kanalnetzbetreiber zeigen, sehr stark eingeschränkt und darüber hinaus von den praktizierten Reinigungsintervallen beeinflusst. |