
|

(Image: 386321 - Titelbild Dokumentation) Process: Lateral connection repair Title: Recovery of lateral connections DN 150 of a sewer DN 250 that was rehabilitated by CIPP using the DrainLCR system Location: Factory premises Limiting conditions:
- System: mixed water
- Material: vitrified clay / plastic
- Nominal size: sewer DN 200 / 250 / 300
lateral DN 150
- gradient: 1‰
- depth position: approx. 0.6 m (≈ 2ft.)
- rehabilitation length: 100 m (≈ 328 ft.), …
|
|

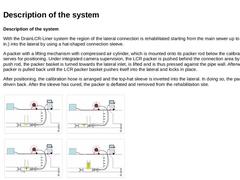
Description of the system With the DrainLCR-Liner system the region of the lateral connection is rehabilitated starting from the main sewer up to 300 mm (≈ 12 in.) into the lateral by using a hat-shaped connection sleeve. A packer with a lifting mechanism with compressed air cylinder, which is mounted onto its packer rod below the calibration hose, serves for positioning. Under integrated camera supervision, the LCR packer is pushed behind the connection … |

|

First, a lateral that leads into the main sewer at an angle of 45° is connected. Preparation of the packer For preparation in a first working step form oil is applied onto the packer, which is equipped with a slightly erected and cleaned calibration hose. A guiding wire is fixed to the end of the balloon of the calibration hose. It is intended to ease the later application of the impregnated top-hat sleeve onto the packer. | (Image: Cleaned and erected … |
|

|

Installation of the top-hat sleeve During the installation of the packer, one member of staff is needed to operate the control unit and another one at the manhole to position the packer by means of the push rods. Important: When transporting the packer to the manhole, care must be taken of the fact that the calibration hose is not damaged. The packer is inserted into the sewer that is to be rehabilitated via the manhole. Before connecting the LCR packer … |

|

Next a lateral, which leads into the main sewer at an angle of 90°, has to be connected. For this purpose, the calibration hose and the packer basket must be replaced. Demounting of the calibration hose In the first working step the connection clamps are removed from both ends of the packer, the LCR string of the pulling-in suite for the balloon of the calibration hose inside the packer is cut and the lid of the winding box is screwed open to remove … |

|

Now, the lateral that leads into the main sewer at an angle of 90° is connected. The rehabilitation process is the same as the rehabilitation process with top-hat sleeves at a connection angle of 45°. It includes: Preparation of the packer - Dabbing the calibration hose with form oil
- Fixing the guiding wire to the balloon of the calibration hose
| (Image: Dabbing the packer with form oil) | (Image: Guiding wire at the end of the balloon of the calibration … |
|

|

Repairing the connection of DN 150 lateral sewers connected to a DN 250 sewer by means of cured-in-place top hat profile (DrainLCR system) (CIPP). |

|

This lecture "Repair" is part of the lecture series "Trenchless 101" and serves to provide an overview of trenchless repair methods for non-accessible drains and sewers. It is mainly about the following method categories: - reparation by means of robot processes
- sealing by means of internal sleeves.
|

|

|
According to EN 752-5 [DINEN752-5:1997], repair is understood to be measures to rectify local damages. (Image: Repair)
|
|

|

|
These repair processes include: |
- Restoration ;
- Injection processes ;
- Sealing processes .
|
| (Image: Overview of the repair processes) |
| (Image: Self-propelling KASRO-operating robot (PROKASRO Mechatronik GmbH)) |
| (Image: Packer and sewer TV camera for Posatryn process) |
| (Image: Completed Partliner™) |
|
|

|

|
Restoration processes are used for local or sectional rectifications or for the replacement of pipes or structural components in order to restore the functionality, the static load bearing capacity as well as the leaktightness. | |
(Image: Structural calculation)
|
|
(Image: Leaktightness)
|
|
(Image: Hydraulic)
|
|
|

|

|
Robot: Remote control device with closed circuit television (CCTV) monitoring, used mainly in localized repair work, such as cutting away obstructions, re-opening lateral connections, grinding and re-filling defective areas and injecting resin into cracks and cavities [NASTT06]. | |
(Image: Repair of a projecting connecting sewer with the KA-TE system [FI-Kunsta])
|
(Image: Sealing a groundwater infiltration with the KA-TE system [FI-Kunsta])
|
|
|
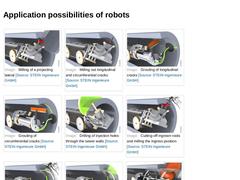
|

|
(Image: Milling of a projecting lateral)
|
(Image: Milling out longitudinal and circumferential cracks)
|
(Image: Grouting of longitudinal cracks)
|
|
(Image: Grouting of circumferential cracks)
|
(Image: Drilling of injection holes through the sewer walls)
|
(Image: Cutting-off ingrown roots and milling the ingress position)
|
|
(Image: Grouting of the ingress position)
|
(Image: Grouting of holes in the sewer wall)
|
(Image: Installation of sleeves)
|
|
|
|

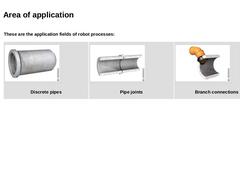
These are the application fields of robot processes: | | (Image: Discrete pipes)
Discrete pipes | (Image: Pipe joints)
Pipe joints | (Image: Branch connections)
Branch connections |
|

|

|
Robot processes are applied to eliminate the following damages: - Radial cracks
- Longitudinal cracks
- Flow obstacles (deposits, foreign substances, root ingress etc.)
- Missing pieces of pipe wall
- Defective pipe connections
- Unprofessional branch connections
| |
(Image: Projecting lateral [FI-Jtele])
|
|
(Image: Root ingress in the region of a pipe joint [FI-KMG])
|
|
(Image: Incrustation [FI-Jtele])
|
| | (Image: Attention!)
The positional stability of the damage … |
|

|

|
(Image: Insertion of robot into manhole)
|
(Image: Camera-controlled positioning of robot)
|
|
(Image: Milling of a crack by means of the KA-TE-milling robot)
|
(Image: Robot with injection head)
|
|
(Image: Grouting of the crack by means of the KA-TE-smoothing robot)
|
(Image: Robot with sleeve)
|
|
Procedure: - The robot is inserted via the closest manhole with access for cleaning and inspection, and its remote-controlled positioning is carried out by …
|
|

|

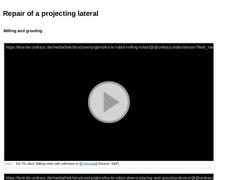
Milling and smoothing |
(Image: Repair of a projecting lateral with KA-TE system - milling of the projecting lateral until it is flush with the internal pipe wall [FI-Kunsta])
|
(Image: Repair of a projecting lateral with KA-TE system - milling of the projecting lateral until it is flush with the internal pipe wall [FI-Kunsta])
|
(Image: Repair of a projecting lateral with KA-TE system - after completing the milling works [FI-Kunsta])
|
|
(Image: Repair … |
|
|
|

|
Milling and grouting |
|
(Video: KA-TE robot: Milling robot) |
|
(Video: KA-TE robot: Sleeve-placing and grouting device) |
|
|
(Video: Repair of a recessed lateral with the KA-TE system [FI-Kunsta]) |
|

|

(Video: Schematic illustration of a grouting system consiting of a folding saddle and a packer)
|
(Image: Rehabilitation of a lateral inlet - view of the retracted packer) |
(Image: Rehabilitation of a lateral inlet - expanded packer) |
(Image: Rehabilitation of a lateral inlet - rehabilitated lateral inlet) |
(Image: Rehabilitation of a lateral inlet - mixing plant for mixing the fibre-reinforced dry gorut) |
|
|

|

|
(Image: Milling of a crack by means of the KA-TE-milling robot)
|
(Image: Milling of a crack by means of the KA-TE-milling robot)
|
|
(Image: Grouting of the crack by means of the KA-TE-smoothing robot)
|
(Image: Smoothing of the grouted crack by means of the KA-TE-smoothing robot)
|
|
|

|

| (Image: Pros and cons) | Advantages of robot processes: - no or only few obstructions of public transport
- no excavation necessary
- low emissions
- repair of almost all damages of sewers possible due to the manifold functions of the robot systems
- no reduction of nominal size
- no or only temporary interruption of drainage capability during the repairing works
|
|

|

| (Image: Pros and cons) | Disadvantages of robot processes: - the purchase costs of the equipment are relatively high
- high level of operator skill required
- a precise evaluation of the damage necessary
|
|

|

|
Sealing processes are understood to be measures for the local sealing of sewers to restore the leaktightness and, if necessary, to stabilise the load bearing capacity. | |
(Image: Structural calculation)
|
|
(Image: Leaktightness)
|
|
|
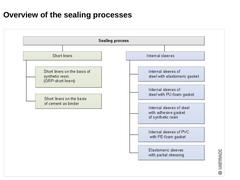
|

| (Image: Overview of the sealing processes from inside by means of internal sleeves)
|
|

|

This process group is characterised by a woven sleeve soaked in synthetic resin, which, with the aid of a packer that is inflatable by air, water or steam, is transported to the damage location in the sewer and pressed against the internal wall of the sewer and is then hardened in situ while the pressure of the packer is maintained. (Video: Working steps in the installation of a short liner) |
|
(Image: Synthetic resin-based short liner - Packer with … |
|