
|
According to DVGW GW 321 [HDD-15] with reference to DVS 2207-1 [HDD-435] and/or ASTM D3261-03 [HDD-436] and ASTM D2657-03 [HDD-437], PE 80 and PE 100-pipes for use in HDD must be connected by heated tool or butt fusion welding (Figure 240) [HDD-438]. In this welding technique, the connection surfaces of the pipes to be welded are heated under pressure at the heating element and are connected after removing the heating element (Figure 239 and Figure … |

|
The destruction-free check of the welding seam can be carried out in three ways according to EN 13100 [HDD-442]: -
visual inspection,
-
X-ray testing,
-
ultra-sonic testing.
Visual inspection checks butt welds according to the following criteria (Figure 243 a): -
The welding beads have to be equally round and clearly visible.
-
All beads are supposed to be of equal size approximately.
-
The bead surfaces have to be smooth.
-
The beads are supposed to be free …
|

|
For the connection of PE-pipes, generally the following welding techniques can be used: -
heated coil socket welding,
-
extrusion welding,
-
heated tool or butt fusion welding.
In heated coil socket welding, electric welding fittings with integrated resistance wires are used for creating a pipe joint. They are electrically charged during welding (Figure 238). Pulling-in the pipe string that is welded by means of heated coil sockets without causing destruction … |

|
If, due to the soil conditions, impermissible mechanical stress of the pipes or damage to the pipe surface (e.g. scratches, point loads and grooves) is expected (which can always be assumed when directly pullingin the pipe string into the borehole) according to [HDD-15], an additional external pipe protection must be used for PE 80- and PE 100-pipes. In order to ensure its protective effects, the outer protective layer must comprise at least 10% of … |

|
(Image: PE 100-pipe with dimensionally added protective coating of minerally reinforced PP of the type egeplast SLM®2.0 (SLM – Safety-Line® host pipe))In order to produce pipes with dimensionally added protective coating, according to DIN 8074 [HDD-431] and DIN 8075 [HDD-417], standard pipes of PE 80 or PE 100 (so-called core pipes) are, in a second production step, separately coated with another material such as mineral reinforced polypropylene … |
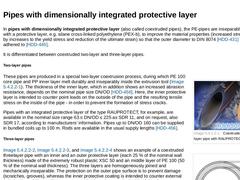
|
In pipes with dimensionally integrated protective layer (also called coextruded pipes), the PE-pipes are inseparably connected with a protective layer, e.g. silane cross-linked polyethylene (PEX-b), to improve the material properties (increased strength values by increases to the yield stress and reduction of the ultimate strain) so that the outer diameter to DIN 8074 [HDD-431] can be adhered to [HDD-445]. It is differentiated between coextruded two-… |

|
If, due to the soil conditions, impermissible mechanical stress of the pipes or damage to the pipe surface (e.g. scratches, point loads and grooves) is expected (which can always be assumed when directly pullingin the pipe string into the borehole) according to [HDD-15], an additional external pipe protection must be used for PE 80- and PE 100-pipes. In order to ensure its protective effects, the outer protective layer must comprise at least 10% of … |

|
Polyethylene (PE) belongs to the group of semi-crystalline thermoplastics (polyolefin). It is marked by a high degree of flexibility and ductility also at low temperatures [HDD-415] [HDD-416]. PE is resistant to acids, alkalis and weak solvents. It is not resistant to oxidising acids and halogens. Further information in this respect is contained in the Addendum to DIN 8075 [HDD-417]. For PE-pipes, which are used in HDD, the following standards apply: |
|
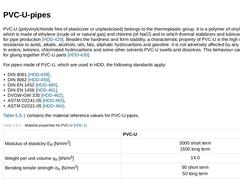
PVC-U (polyvinylchloride free of plasticizer or unplasticised) belongs to the thermoplastic group. It is a polymer of vinyl chloride, which is made of ethylene (crude oil or natural gas) and chlorine (of NaCl) and to which thermal stabilizers and lubricants are added for pipe production [HDD-429]. Besides the hardness and form stability, a characteristic property of PVC-U is the high degree of resistance to acids, alkalis, alcohols, oils, fats, aliphatic … |

|
The restrained joint of PVC-U pipes can be achieved by means of a socket, weld or glued connection (see (Type and design of the joints)). The latter variant is not used for HDD applications, because professionally completed glued connections require around 12 hours to harden completely and to be able to reliably bear longitudinal forces resulting from the pulling-in of the pipe [HDD-465]. |

|
The restrained joint of PVC-U jacking pipes is achieved by means of a special, rigid or flexible plugin socket joint, in which a mechanism prevents the joint from being pulled apart. The restrained joint in its rigid variant can be of two types, for example, with the manufacturer CertainTeed [HDD-469] (see (Restrained socket or spigot joints)): -
Joining of both plug-in ends with a coupling, where a milled groove each in the outer wall at the plug-in …
|

|
For creating welded joints with PVC-U pipes, heated tool or butt fusion welding is used (Figure 254a and b). The welding process principally resembles that of PE-pipes (see (Heated tool or butt fusion welding)), however, there are essential differences regarding welding temperature, jointing pressure and duration of the single steps [HDD-472]. (Image: Creation of a pipe joint for PVC-U-pipes (12’’, SDR-18, type Fusible C900™) by means of heated element … |

|
The restrained joint of PVC-U pipes can be achieved by means of a socket, weld or glued connection (see (Type and design of the joints)). The latter variant is not used for HDD applications, because professionally completed glued connections require around 12 hours to harden completely and to be able to reliably bear longitudinal forces resulting from the pulling-in of the pipe [HDD-465]. |

|
Due to the high abrasion and corrosion resistance (cf. Annex 1 of DIN 8061 [HDD-458]) of PVC-U, special measures to protect the pipe surfaces during pulling-in, such as jacketing, are not necessary. |

|
Figure 255a and b show a special development based on multiple installation in the form of group installation (see Section 2.2.3 in Volume 1 [HDD-1]). Here, special PVCU host pipes with thrust-restrained joints (plug-in joint with socket and spigot end), which allows a 150 m (164 yards) long pipe string to be pulled-in by HDD, are used. Three or four PVC-U cable casing pipes, which during jointing the pipe sections are connected by means of a special … |

|
PVC-U (polyvinylchloride free of plasticizer or unplasticised) belongs to the thermoplastic group. It is a polymer of vinyl chloride, which is made of ethylene (crude oil or natural gas) and chlorine (of NaCl) and to which thermal stabilizers and lubricants are added for pipe production [HDD-429]. Besides the hardness and form stability, a characteristic property of PVC-U is the high degree of resistance to acids, alkalis, alcohols, oils, fats, aliphatic … |

|
According to DIN EN 14457 [HDD-294] and/or DIN EN 805 [HDD-296], a pipe is a “component of uniform bore, normally straight in axis, having e.g. socket, spigot or flanged ends.” The pipes that are pulled into the usually expanded borehole when using HDD (pulling-in process, see (Method of operation and sequence)), can be classified among the category of jacking pipes. In the following discussion, jacking pipes will be understood to be prefabricated … |

|
|
Abrasiveness |
The characteristic of soil and rock to cause a larger or smaller amount of wear of the excavation tool during boring. [HDD-viii] |
|
Air-(gas)-flushing |
The spoil is displaced, respectively removed, with a circulating flushing medium based on compressed air (gas) without or with addition of foam formers. [HDD-viii] |
|
Air-(gas)-flushing directional drilling |
Direct liquid flushing with a gaseous flushing medium for the installation of pipes … |
|

|
Developed from directional and deep drilling technology, HDD as a steerable drilling method is ideal for the trenchless installation of pipelines. Utilities and communications providers make use of the numerous advantages of this technology, as it provides a customized variant for almost every problem within the scope of its possibilities. However, it is precisely these variants that make it necessary to systematically cover the full range of HDD technology. The book provides valuable guidance and decision support on the topics of equipment, steering and locating techniques, project preparation and planning, structural calculations for the state of construction and operation including: pullback force, buoyancy and ballasting, safety against buckling, pipe stresses, abutment and bedding. Special process developments such as Meeting-in-the-Middle technique, PTT "Push and Pull Technology", COMBI DRILLING method and hybrid systems are described in detail as well as drilling fluids, dry horizontal directional drilling and pipe materials and joints. |