|

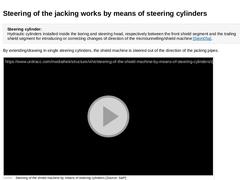
Steering cylinder:
Hydraulic cylinders installed inside the boring and steering head, respectively between the front shield segment and the trailing shield segment for introducing or correcting changes of direction of the microtunnelling/shield machine (not found). By extending/drawing in single steering cylinders, the shield machine is steered out of the direction of the jacking pipes. (Video: Steering of the shield machine by means of steering cylinders) |

|

|
|

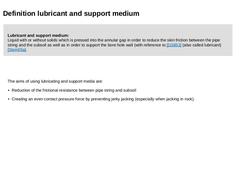
Lubricant and support medium:
Liquid with or without solids which is pressed into the annular gap in order to reduce the skin friction between the pipe string and the subsoil as well as in order to support the bore hole wall (with reference to [DS853] (also called lubricant) [Stein05a]. |
The aims of using lubricating and support media are: |
|

|

Mixing plant:
A mixing plant (also called mixing unit) serves for creating support fluids (suspensions) and lubricants. In the mixing plant the suspension base (water) is mixed with additives (bentonite, polymers, etc.) [Stein05a]. (Image: Mixing plant with supply pump) |

|

Mixers are available in various sizes and consist mostly of: -
Drive unit (diesel or electrically driven)
-
Mixing container and, if necessary, additional container(s)
-
Drilling fluid pump(s)
Most mixing plants are designed in a modular fashion in order to be able to be placed into service in a relatively simple and flexible fashion with reference to the required capacity. This approach also allows easy combinations with separation plants. (Image: Model … |

|

|
(Image: Lubrication station) |
Injection:
Insertion of grouts (pressing-in and filling material) into cracks and cavities under pressure via injection sockets or nozzles (also called grouting) (with reference to [DS853]) [Stein05a]. |
|
Grouting:
Grouting is understood as the insertion of injection material into underground cavities under pressure [Stein05a]. |
|

|

|
(Image: Attention!)
The pressing of the lubricant and support medium into the annular gap is also referred to as injection or grouting. The aim is to produce a continuous lubricating film between the pipe and the subsoil, thus reducing the frictional resistance between both. Ideally, the lubricant and support medium should completely fill the annular gap so that the pipe string floats. |
Prerequisites for creating a continuous lubrication are: |
|

|

As regards the injection technology, a differentiation is made between: -
Injection/grouting in the region of the boring head
-
Injection/grouting through injection nozzles in a non-man-accessible pipe string with two-phase jacking
-
Injection/grouting through injection nozzles by hand in a man-accessible pipe string
-
Automatic injection/grouting through injection nozzles in the pipe string
(Image: Lubricating the pipe string in the ULTIMATE METHOD (… |

|

|
(Image: Lubricating the pipe string in the ULTIMATE METHOD (Bild 9.5.2) with reference to [FI-Kidoh] [Image: S&P GmbH] - Grouting the lubricating and support medium in the boring head region by means of a special distribution ring) For even distribution of the lubrication and support medium about the pipe circumference, some microtunnelling/shield machines have a distribution ring arranged at the periphery of the shield cutting edge with corresponding … |
|

|

The manual injection in an accessible pipe string can also be referred to as manual lubrication. The lubricant is injected into the annular gap by manually activated upstream valves via individual injection nozzles which are evenly installed in the pipe circumference and the pipe string. This procedure is today only applied in very short tunneling sections, especially with shield machines with partial excavation. Disadvantages of manual grouting via … |

|

|
(Image: T.B.K. system for lubricating the jacking string with reference to [FI-TBKa] [Image: S&P GmbH]) |
(Image: Attention!)
Automatic lubrication systems are characterized by good economics as the personnel that would be needed for this activity are not required [Schwa00]. |
|
For automatic grouting via injection nozzles, the following lubricants are used: -
bentonite suspensions
-
polymer-based solutions.
In long distance and curved jacking, automatic … |
|

|

Common values in practice, for instance, are a maximum of 5 bar injection pressure or 20 second injection duration per grouting nozzle. The spacing of the so-called lubrication stations - jacking pipes with works-installed injection nozzles - is based on experience and, when using a bentonite suspension as lubrication and support medium, and for long jacking distances, is between 9 to 15 m. Example: Every third jacking pipe (3 m) is equipped with … |

|

|

|

The following possibilities are available with pipe jacking for the removal of spoil taking into account the type of shield machine, the nominal pipe size and the jacking distance: -
Continuous conveyor (belt conveyor, chain conveyor, hydraulic and pneumatic conveyors)
-
Operation without rails using transport carts, conveying buckets with winch systems or self-propulsion
-
Tracked transport carts with winch systems or self-propulsion (floor-mounted …
|
|

|

|

|

(Image: Technical components in pipe jacking - separation plant) Separation plants:
In all cases where flushing is based on bentonite, it is necessary to utilize a separation plant for cleaning and reclaiming the bentonite suspension and dewatering the spoil in order to make it fit for disposal. |

|

The separation of solids particles from the flushing medium is carried out in several steps in the separation plant corresponding to the particle fraction of the spoil, for instance by means of: -
coarse separation by sieving
-
medium separation in hydrocyclones (single or multi-step)
-
fine material separation, for instance, in centrifuges or chamber filter presses.
As a rule, the first two methods mentioned above are always used. … |

|

|
Separation plant:
Installation for the mechanical separation of the components solid (spoil) and liquid (liquid drilling fluid) in order to provide the drilling fluid again for the conveying circuit and to make the gained spoil disposable. The separation of solid particles from the drilling fluid is carried out by sedimentation techniques or multistage separation techniques corresponding to the in-situ particle fractions of the soil (based on [… |
|

|

(Video: Schematic illustration of a two-stage hydrocyclone separation plant with subsequent centrifuge) Video: Schematic illustration of a two-stage hydrocyclone separation plant with subsequent centrifuge with reference to [Rubar99] [Image: S&P GmbH]. This interactive object is only visible online. |

|

|

|

Today, the installation of gas, water and wastewater pipelines is still predominantly carried out using open trenches. In view of the numerous disadvantages associated with this method, it is imperative that trenchless pipeline construction be considered much more strongly in the future than it has been to date as an alternative in the planning and construction of sewers and pipelines.
This module deals in detail with the procedure and the various components. Emphasis is placed on the different types of shield machines, excavation tools, separation systems, the control and steering station, injection/grouting agent and soil extraction and reprocessing.
After completing this module, you will have a sound knowledge of:
- all components of pipe jacking and
- their function and tasks.
|

|

Today, supply and discharge lines are still predominantly installed by using the open-cut method: a trench is dug, the lines are installed. Under the protection of an embankment or sheeting and the trench is filled afterwards. In the face of the numerous disadvantages as well as the citizens' growing environmental consciousness in the future it is urgently necessary to take trenchless technology into account much stronger than until today as an alternative … |

|

|
(Image: Unmanned techniques) |
|
(Image: Steerable techniques) |
|
Microtunnelling:
Microtunnelling refers to unmanned, remote-controlled techniques for pipe jacking (jacking pipe ID < 1200 (48 in)) in which, for reasons of machine technology and occupational health and safety, the use of personnel on the working face during jacking is prohibited. This also applies during troubleshooting for example when the jacking is at a standstill. |
Microtunnelling |
|

|

|
(Image: Unmanned techniques) |
|
(Image: Steerable techniques) |
|
(Image: Soil removal techniques) |
|
(Image: Soil displacement techniques) |
|
In microtunnelling methods, jacking pipes are jacked (in one or two phases) from a starting shaft with the aid of a jacking station (in exceptional cases also using additional intermediate jacking stations) up to a target shaft. At the same time an unmanned, remote controlled microtunnelling machine carries out … |
|
|

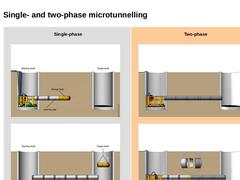
Single-phase |
(Image: Single-phase jacking - Jacking)
|
|
(Image: Single-phase jacking - Completed pipeline)
|
| Two-phase |
(Image: Two-phase jacking - Phase 1)
|
|
(Image: Two-phase pipe jacking - Phase 2)
|
|
|